Natural Drug Discovery Company

Nephrine

Pishak, V. P., Rogovoy M. V. “Pathophisiology of the Chronical Nephritic Masugi”. Book, Chernivci, “Mistro”, 1008, 168 pages, 2011.
The given monograph presents theoretical general conclusion and new solution of scientific problems concerning pathogenesis of tubule-interstitial syndrome as the basis of development of chronic and quickly progressing pathological process in the cortical, medullar substance and papillae of the kidneys under conditions of chronic Masugi nephritis (nephrotoxic serum nephritis).
NEPHRINE preparation under conditions of development of tubulo-interstitial syndrome in case of chronic Masugi nephritis demonstrates its protective influence on the equilibrium of regulatory processes in the cortical substance and kidney papilla, with revealed in the prevention of spread of the connective tissue in the kidney interstitium; obturation processes on the level of kidney papilla and inhibits development of glomerulosclerosis.
V.P.Pishak, Yu.E.Rohovyy, I.I.Sidorchuk, L.G.Arkhipova, I.L.Muraviyova, A.V.Bocharov, M.V.Khalaturnik
Department of Physiology at Bukova State Medical University, Tchernovtsy,
Ukraine, 58001,
e-mail: yuriy_rohovyy@rambler.ru
Analysis of the protective effects of GA-GLOMURONEFRIN medication during sublimate nephropathy with a vegetative resonance test “Imedis Test +”`
.
The nature of functional overripe of the kidneys and hormonal-messenger system of sodium-ion homeostasis at the time of damage of proximal section of the NEPHRINE by the sublimate, due to depression of SH-group Na+-K+ ATP-ase enzymes, succinate dehydrogenase and Aquaphorine 1 protein with the following activation of tubule-glomerular mechanism of feedback has been well-investigated both at oliguric and polyuric stages of the whole process In addition, there is the rising interest over the time to the investigations of the functional state of kidneys and hormonal-messenger system of sodium-ion homeostasis using vegetative-resonance test “Imedis Test+” , and use of NEPHRINE preparation due to ability of harmonization among processes (sympathetic – catabolism – acidity) or (parasympathetic – anabolism – alkalinity). However, protective effect of NEPHRINE upon the correction of sublimate nephrophatic state has not been (in any terms) investigated.
Purpose of the research was to investigate opportunities of protective diagnostic abilities of NEPHRINE preparation during sublimate nephropathy in rats with vegetative-resonance test “Imedis Test+” at water diuresis.
Materials and Methods
In the experiments with 24 white mail mature rats with sublimate nephropathy (administration of 0.1% sublimate solution at 5 mg/kg dosage), protective effects of NEPHRINE preparation have been investigated (daily administration at 2 mkg/kg dosage) at oliguric (24 hours) and polyuric (72 hours) stages of acute renal failure. Function of the kidneys has been explored during artificially induced water diuresis. For this purpose rectal drip of warmed tap water (37 Co) has been introduced at 5% of body weight volume. Urine was collected within two hours. During the urine assessment with using vegetative-resonance test “Imedis Test+”, samples were investigated within bio-resonance cameras of electric-punctuation diagnostic apparatus “Mini-Expert T” (Registration certificate on technical characteristics of medical product N FS 022a3065/0415 issued by Federal Service of supervision in Health and Social Development of Russian Federation, dated July 2004) and estimated at bio-index scale for Creatinin, Sodium ions, Potassium, Lithium, Urea, Thromboxan A, Aldosterone, protein, PgE2, Angiotensine 2, TNF-a, L-Arginine, vasointestinal peptide, NEPHRINE medication. Life-time testing of creatinin in blood and sublimate in cortical substance of the rat kidneys, as well as PgE, angiotensine 2., TNF-a, L-arginine, vasointestinal peptide was performed through the reproductive biologically active point of healthy volunteer at direct contact of the one with experimental animal .
Investigation material has been processed using parametric statistics through programming package of “Star graphics” and “Excel-7.0”.
Results
At oliguric stage of sublimate nephropathy in rats NEPHRINE preparation caused tendency to increased diuresis with additional decreased content of Creatinin, Sodium ions, Potassium, Lithium, Urea, Thromboxan A2, Aldosterone, protein, PgE2, Angiotensine 2, TNF-a, L-Arginine, vasointestinal peptide in urea. Concentration of sublimate was increased and NEPHRINE medication tested (Scheme).
At polyuric stage of sublimate nephropathy NEPHRINE medication promoted decrease of renal azotermia lowering creatinin concentration in blood plasma, sublimate, Angiotensine 2, Thromboxan A2, TNF-α, L-Arginine, PGE2, VIP in cortex renalis (Table 91).
Table 91.
Influence of medicine NEPHRINE and an antioxidant of Ionol on biochemical indicators of different sections of a liver of rats at a sharp of hemic hypoxia in 2 hours after an injection of sodium of the nitrite, investigated with use "Imedis Test +" (х Sx)
1. conventional unit – (CU) p< 0,00
Correlation analysis revealed primary interconnection between blood creatinin – sublimate of renal cortex and PgE2, sublimate of renal cortex -- TNF-α of kidney cortex (Table 92).
Table 92.
Influence of NEPHRINE on creatinin concentration in blood plasma, sublimate content, TNF-a and hormonal-messenger systems of sodium-ion homeostasis in cortex substance of the kidneys during polyuric stage of sublimate nephropathy during the experiments on rats with the help of vegetative-resonance test “Imedis Test” (X+- m)
R – distinction reliability in the comparison with the sublimate nephropathy
Discussion
Protective effect of NEPHRINE preparation is determined by its ability of harmonized relations among processes (sympathetic – catabolism – acidity) or (parasympathetic – anabolism – alkalinity). As the result, damage of proximal section of the nephrone with sublimate (mercury dichloride) diminishes, which is verified by the increase of sublimate in the urine, decrease of protein content, sodium and lithium ions (lithium ions are re-absorbed exclusively in proximal section of the nephrone). Decrease of the damaging action of sublimate on proximal section of the nephrone is accompanied by the decrease in sodium ions delivery to macula densa distal section of the nephrone with the diminished reactivity of tubulomerular reverse connection (feedback) and ischemic activation of lipid peroxidation in kidney cortex that was indicated decrease of Angiotensine 2 and Thromboxan A2 in urine. Decrease of PGE2, VIP and L-Arginine indicates lowering of vasodilator tone in response to weakened tone of vasoconstrictors Angiotensine 2 and Thromboxan A2. Decrease of creatinin concentration and urea in the urine points to diminished intensity of renal azotermia because of protective influence of NEPHRINE medication.
Revealed decrease of sublimate content and TNF-α within renal cortex at polyuric stage of sublimate nephropathy points to protective effect of NEPHRINE medication at proximal section of the nephrone. This processes is accompanied by lowered reactivity of tubular-glomerular reverse conjunction with the decreased content of vasoconstrictors Angiotensine 2 and Thromboxan A2 in renal cortex with weakened renal azotermia to creatinin content in blood plasma. Lowered content of vasodilators PgE2, VIP and L-Arginine in cortex of the kidneys points not only to the absence of re-perfusional injury of kidneys towards the influence upon NEPHRINE medication, but, most probably, to polyuric stage itself because of elimination of preliminary complex injury of kidneys against treatment background of the given preparation.
Positive correlative connection between sublimate content and blood creatinin is determined by the development of retentive azotermia because of the damage of proximal nephrone and activation of tubulo-glomelural biofeedback. Primary correlative dependence between PgE2 and TNF-α at polyuric stage of sublimate nephropathy is determined by reperfusional damage of proximal tubule.
Table 93.
Correlative analysis of connections between creatinin concentrations, sublimate content and PgE2 in cortex substance of kidneys 72 after sublimate administration at the examination of rats with vegetative-resonance test “Imedis Test+”
Influence of NEPHRINE medication at the course of sublimate nephropathy in rats at oliguric stage of pathology development, 24 hours after administration of mercurial dichloride with vegetative-resonance test “Imedis Test+”. 1- Sublimate nephropathy; 2- Sublimate nephropathy + nephrone. Reliability of the differences in comparison with sublimate nephropathy is mentioned as ***. p<0,01; **** p<0,001
Conclusion
NEPHRINE medication has protective influence during sublimate nephropathy both at oliguric and polyuric stages of pathology, accompanied by accelerated sublimate excretion with urine from the organism, decrease of its content in kidney cortex, lower rate of retentive azotermia due to the normalization of the balance of hormonal-messenger systems of sodium-ion homeostasis. Method of vegetative-resonance test “IMEDIS TEST” gives us the possibility to reveal presence of preliminarily administered nephrone medication in rats’ urine. Perspective of scientific investigations lays in permanent use of the vegetative-resonance test “Imedis test+” for the life-time assessment of biological parameters of experimental animals with kidney diseases.
Functional state of the kidneys during water diuresis, loading with 3% sodium chloride and analysis of the protective influence of NEPHRINE medication at sublimate nephropathy, Masugi nephritis with the use of vegetative-resonance test “Imedis Test”.
Prof. Rohovyy Yurii Evgenyi, Arkhipov Ludmila Georgii, Muraviov Irina Lev
O. Kobilyanskyi str. 53/2. Tschertovtsy, Ukraine. 58001,
e-mail: yuriy_rohovyy@rambler.ru
ALEXIS Co. Georgia, Tbilisi.,
Bukova State Medical University (Tschernovsky), Ukraine.
Center for Intellectual Medical Systems “IMEDIS” (Moscow) of Russian Federation.
In the experiments on 64 white mature mail rats with vegetative-resonance test “Imedis Test” life-time diagnostic methods of biological parameters in internal organs of experimental animals have been elaborated.
Investigation of the function of the kidneys and hormonal-messenger systems of sodium ion homeostasis using vegetative-resonance test “Imedis Test” has shown identical rearrangements of above-mentioned parameters during comparison of two regimes: 1) water diuresis (minimum level of ADG, urine osmosis ~ 50 mosm/kg and 2) Load with 3% sodium chloride (maximum ADT level, urine osmosis ~ 1200 mosm/kg in comparison with familiar objective methods.
Also, increase of the concentrations of organic osmolites – betaine, taurine, glycine, sorbitol, proline, and glutamine – has been shown in our experiments during the load of 3% sodium chloride in comparison to water diuresis.
Protective effect of GA-40 medication (complex of highly purified proteins of plant origin) was shown during sublimate nephropathy both at oliguric and polyuric stages during pathological process development. This was characterized by the increased excretion of sublimate with urine, decrease of its content within cortex substance of the kidneys, lowered level of renal azotermia and normalization of the balance of hormonal messenger systems of sodium ion homeostasis. Method of vegetative-resonance test “Imedis Test” makes possible to determine NEPHRINE preparation in the urine of rats, which has been administered preliminarily (in advance).
By the 30th day of sublimate nephropathy, tubulo-intersticial syndrome was revealed in cortex, medulla, papillary layer of kidneys that was proved hystologically, enlargement of the crystal substance (collagen marker) and amorphyc substance (marker of the atrophy of kidney tubules) towards the use of correlative-optical methods of kidney investigation.
NEPHRINE medication has anti-nephrosclerotic effects in these circumstances that are accompanied by the normalization of the levels of crystal amorphyc substances and their correlation.
At 45th day of chronic Masugi nephritis increase of collagen-marker-oxyproline and pro-apoptic protein p53 (marker of channel atrophy and nephrone glomerulosa) has been shown in cortex substance of kidneys.NEPHRINE medication reveals anti-nephrosclerotic preventive influence (effects) in such conditions.
Experimental Generalisation of Anti-Nephrosclerotic Effects of NEPHRINE at Tubulo-Intersticial Syndrome
Yu. E. Rohovyy, L. G. Arkhipova, I. L. Muravyova, V.G. Savka, M. V. Dikal
Department of Physiology at Bukova State Medical University, Tchernovtsy,
Ukraine, 58001,
e-mail: yuriy_rohovyy@rambler.ru
Purpose of the research – clarification of protective abilities of NEPHRINE preparation (complex of highly purified plant proteins) at the development of tubulo-intersticial syndrome in rats with vegetative-resonance test “Imedis Test”, histological method and correlative-optical research of the kidneys.
Experiments have been carried out on 80 white non-linear mail rats with 0, 16-0, 18 kg weight. Masugi nephritis has been modified by the intra-peritoneal introduction of rabbit nephrone-toxic serum with the titer of anti-renal antibodies, in the reaction of complement-binding no less than 1:1024. Research was carried during 45 days in accordance to the development of chronic Masugi nephritis with tubulo-intersticial syndrome. Death lethal injection of the animals has been implemented with decapitation under ether anesthesia. For the morphological evidence of the development of chronic nephritis and tubule-interstitial syndrome, histological research of the kidney cortex substance has been implemented by the coloring of de-paraffined specimen sections with hematoxylin-eosin and Slinchenko et. al. Sublimate nephropathy was modeled by the administration of 0, 1% sublimate at 5 mg/kg dosage with the research during formation period of tubulo-intersticial syndrome (at 30th day) .
A protective effect of NEPHRINE preparation was investigated administering one in 2mkg/kg dosage. At the evaluation of kidney cortex 50-100 mg sections samples from the rats with vegetative-resonance test “Imedis Test+”, samples in thin organic-glass test-tubes were analyzed in the container of “Imedis BRT PK” apparatus with the use of programming means (Registration certification (Registration certificate on technical characteristics of medical product N FS 022a3065/0415 issued by Federal Service of supervision in Health and Social Development of Russian Federation, dated July 2004) with the estimation at bio-index scale: Angiotensine – 2, Oxyproline, protein p53. Correlative-optical investigation of the kidneys has been implemented .
At 30th day of sublimate nephropathy formation of tubulo-intersticial syndrome has been registered in cortical, medullar and papillary substance of kidneys that has been noticed by the increase of crystal substance (as collagen marker) and decrease of amorphyc one (as the reflection of the atrophy of nephrone segments) . In these conditions NEPHRINE was revealing anti-nephrosclerotic effect on each and every layer of kidneys that was accompanied by the normalization of the level and correlation of amorphyc and crystal substances.
Tubulo-intersticial syndrome has also been diagnosed at 45th day of chronic Masugi nephritis, that became apparent with interstitial fibrosis and atrophy of nephrone tubules. In the cortex substance of the kidneys rising level of collagen marker – oxyproline and pre-apoptic protein p53 was diagnosed with IRT “Imedis Test+”. NEPHRINE medication was revealing anti-nephrosclerotic prophylactic effects in such conditions.
Protective effect of NEPHRINE is due to ability of harmonization among processes (sympathetic – catabolism – acidity) or (parasympathetic – anabolism – alkalinity). As the result, vasoconstrictor collagen-stimulating potential of Angiotensine 2 and Thromboxan A2 diminishes. NEPHRINE medication effect determines its anti-nephrosclerotic influence during chronic period of Masugi nephritis, sublimate nephropathy and prevents atrophy of nephrone tubules and glomerular over the processes of the apoptosis.
Crystal substance, %, cortical layer of the kidneys
Crystal substance, %, medullar layer of the kidneys
Crystal substance, %, papillary of the kidneys
Amorphyc substance, %, cortical layer of the kidneys
Amorphyc substance, %, cortical layer of the kidneys
Amorphyc substance, %, cortical layer of the kidneys
Amorphyc/crystal substance, unit %, cortical layer of the kidneys
Amorphyc/crystal substance, unit %, cortical layer of the kidneys
Amorphyc/crystal substance, unit %, cortical layer of the kidneys
Protective influence of NEPHRINE medication due to development of tubulo-intersticial syndrome at 30th day of sublimate nephropathy according to the data of correlative-optical investigation of the kidneys. 1- Control (Intact animal), 2-Tubule-intersticial syndrome, 3- Tubule-interstitial syndrome at NEPHRINE medication background.
Distinctive reliability is shown as ****-p<0,001 in comparison with the control. -p<0,001 in comparison with tubulo-intersticial syndrome at 30th day of sublimate nephropathy.
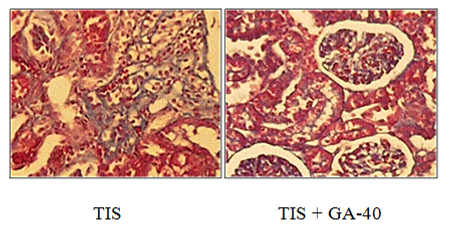
Tubule-interstitial fibrosis of the kidneys cortical substance, glomerular sclerosis and beginning of capsule invagination above nephrosclerotic area at 45th day of chronic Masugi nephritis. Coloring: Slinchenko et. al. mag. : x 56.
Anti-nephrosclerotic effect of NEPHRINE medication on cortical substance of the kidneys at 45th day of chronic Masugi nephritis. Coloring: Slinchenko et. al. mag. : x 56.
Oxyproline, conventional unit, cortical layer of the kidneys
P53 protein, conventional unit, cortical layer of the kidneys
Protective effects of NEPHRINE preparation due to development of tubulo-intersticial syndrome at 45th day of chronic Masugi nephritis according to the data from testing with vegetative-resonance test “Imedis Test+”. 1- Control (Intact animal), 2-Tubule-intersticial syndrome, 3- Tubule-interstitial syndrome at NEPHRINE medication background.
Distinctive reliability is shown as ****-p<0,001 in comparison with the control. ***-p<0,001 in comparison with tubulo-intersticial syndrome at 45th day of chronic Masugi nephritis.
Conclusions
-
Protective anti-nephrosclerotic influence of NEPHRINE medication at the development of tubulo-intersticial syndrome has been proved hystologically with the correlative-optical diagnosis method and vegetative-resonance test “Imedis Test+”.
-
Anti-nephrosclerotic influence of NEPHRINE medication at tubulo-intersticial syndrome prevents tubular and glomerular atrophy of the kidneys that are determined by the activation of apoptosis, which is accompanied by lowered pre-apoptic protein p53 and collagen marker – Oxyproline.
Perspective of scientific investigations lays in permanent use of the vegetative-resonance test “Imedis test+” for the life-time assessment of biological parameters of experimental animals with kidney diseases.
Pahophysiological Analysis of the Diagnosis of NEPHRINE Medication Protective Activity During Sublimate Nephropathy in Rats with Vegetative-Resonance Test “Imedis Test+”
U. E. Rohovyy, L. G. Arkhipova, I.L. Muravyiova, A. B. Popovich
Department of Physiology at Bukova State Medical University, Tchernovtsy,
Ukraine, 58001,
e-mail: yuriy_rohovyy@rambler.ru
Purpose of the research: investigation of the diagnostic opportunities of protective abilities of NEPHRINE preparation during sublimate nephropathy in rats with vegetative-resonance test “Imedis Test+” at water diuresis.
In the experiments with 24 white mail mature rats with sublimate nephropathy (administration of 0.1% sublimate solution at 5 mg/kg dosage), protective effects of NEPHRINE preparation have been investigated (daily administration at 2 mkg/kg dosage) at oliguric (24 hours) and polyuric (72 hours) stages of acute renal failure.
At oliguric stage of sublimate nephropathy in rats with low sodium group NEPHRINE preparation caused tendency to increased diuresis with additional decreased content of Creatinin, Sodium ions, Potassium, Lithium, Urea, Thromboxan A2, Aldosterone, protein, PGE2, Angiotensine 2, TNF-α, L-Arginine, vasointestinal peptide in urea. Concentration of sublimate was increased and GA-40 medication tested.
At polyuric stage of sublimate nephropathy NEPHRINE medication promoted decrease of renal azotermia lowering creatinin concentration in blood plasma, sublimate, Angiotensine 2, Thromboxan A2, TNF-α, L-Arginine, PGE2, VIP in cortex renalis. Correlation analysis revealed primary interconnection between blood creatinin – sublimate of renal cortex and PgE2, sublimate of renal cortex -- TNF-α of kidney cortex.
Protective effect of NEPHRINE preparation is determined by its ability of harmonized relations among processes (sympathetic – catabolism – acidity) or (parasympathetic – anabolism – alkalinity). As the result, damage of proximal section of the nephrone with sublimate (mercury dichloride) diminishes, which is verified by the increase of sublimate in the urine, decrease of protein content, sodium and lithium ions (lithium ions are re-absorbed exclusively in proximal section of the nephrone). Decrease of the damaging action of sublimate on proximal section of the nephrone is accompanied by the decrease in sodium ions delivery to macula densa distal section of the nephrone with the diminished reactivity of tubulomerular reverse connection (feedback) and ischemic activation of lipid peroxidation in kidney cortex that was indicated decrease of Angiotensine 2 and Thromboxan A2 in urine. Decrease of PgE2, VIP and L-Arginine indicates lowering of vasodilator tone in response to weakened tone of vasoconstrictors Angiotensine 2 and Thromboxan A2. Decrease of creatinin concentration and urea in the urine points to diminished intensity of renal azotermia because of protective influence of NEPHRINE medication.
Revealed decrease of sublimate content and TNF-α within renal cortex at polyuric stage of sublimate nephropathy points to protective effect of NEPHRINE medication at proximal section of the nephrone. This is accompanied by lowered reactivity of tubular-glomerular reverse conjunction with the decreased content of vasoconstrictors Angiotensine 2 and Thromboxan A2 in renal cortex with weakened renal azotermia to creatinin content in blood plasma. Lowered content of vasodilators PgE2, VIP and L-Arginine in cortex of the kidneys points not only to the absence of re-perfusional injury of kidneys towards the influence upon NEPHRINE medication, but, most probably, to polyuric stage itself because of elimination of preliminary complex injury of kidneys against treatment background of the given preparation.
Positive correlative connection between sublimate content and blood creatinin is determined by the development of retentive azotermia because of the damage of proximal nephrone and activation of tubulo-glomelural biofeedback. Primary correlative dependence between PgE2 and TNF-α at polyuric stage of sublimate nephropathy is determined by reperfusional damage of proximal tubule.
Conclusion
-
NEPHRINE medication has protective influence during sublimate nephropathy both at oliguric and polyuric stages of pathology, accompanied by accelerated sublimate excretion with urine from the organism, decrease of its content in kidney cortex, lower rate of retentive azotermia due to the normalization of the balance of hormonal-messenger systems of sodium-ion homeostasis.
-
Method of vegetative-resonance test “Imedis Test+” gives us the possibility to reveal presence of preliminarily administered NEPHRINE medication in rats’ urine.
New Possibilities of Correlating-Optical Investigation of Renal Tubulo-Interstitial Syndrome in Traumatology
Rohovyy Yu. Ye., Arhypova L. G., Muravieva I. L., Savka V. G., Dikal M. V.
Company ALEXIS, Georgia, Tbilisi
Bukovina State Medical University
(Chernovtsy) Ukraine, 58001,
E-mail: yuriy_rohovyy@rambler.ru
The Centre of Intellectual Medical Systems “IMEDIS”
(Moscow) Russian Federation
Chronic injury of the kidneys with the development of tubulo-intersticial syndrome occurs under conditions of the development of traumatic disease. The authors have demonstrated an excrescence of the connective tissue with an increase of the oxyproline content in experiments on 50 albino nonlinear male rats under conditions of simulating renal tubulo-inetrsticial syndrome that is verified by the use of correlation-optical diagnostics with an increase of the crystaline substance content and a decrease of the amorphos one. The revealed disturbances are accounted for by an excrescence of the optically active conntective tissue in the intersticium, a thikening of the basal membranes of the renal tubules and fibrous transformation of nephrocytes. An elevation of the content of the crystalline substance and a decrease of the amorphous one has been shown in the medullatory substance. The disclosed disturbances are accounted for by an excrescence of the optically active connective tissue along the medullary beams and a fibrous transformation of nephrocytes. Under conditions of the development of tubulo-interstitial syndrome an excrescence of the connective tissue was found to occur in the renal papilla and that was confirmed by correlating-optical diagnostics with an elevation of the content of the crystalline substance and a dicrease of the content of the amorphous one. These disturbances are due to an excrescence of the optically active connective tissue in the interstitial tissue in concequence of a fibrous transformation of the interstitial cells of type II. The use of the NEPHRINE brought about a normalisation of the charachteristics of intersity, ellipticity, the index of birefrigence of the crystalline substance: of the median value, dispersion, asymmetry, mexcess in the cortical, medullary substance and renal papilla that prevented the development of tubulo-interstitial syndrome. A-asymetry and E-excess are more sensitive criteria for an evaluation of the antinephrosclerotic effect of the NEPHRINE in case of tubulo-interstitial syndrome than M-the median value and D-dispersion according to the degree of an influence on the content of the crystalline substance as a collagen marker.
Pathophysiological Analysis of Correlation-Optical Diagnostics of Tubulo-Interstitial Syndrome as the Basis of the Development Process in the Kidneys
Prof. Rohovyy Yurii Evgenyi, Arkhipova Ludmila Georgii, Muraviova Irina Lev, Bocharoff A. V.
Bukovina State Medical University (Tschernovsky), Ukraine, 58001,
E-mail: yuriy_rohovyy@rambler.ru
Center for Intellectual Medical Systems “IMEDIS” (Moscow) of Russian Federation
The study of new methods of diagnostics and treatment of tubulo-interstitial syndrome (TIS) (associated pathology of the renal tubules and intersticium) as a cause of rapid progression and development of a chronic pathological process in the kidneys is one of the topical problems of modern nephrology. This report has presented new opportunities of diagnosing tubulo-interstitial syndrome in an experiment by means of using the methods of correlation-optical diagnostics, vegetative resonance test “Imedis Test +” and has studied the protective effects of a new generation immunocorrector – the NEPHRINE medication (a complex of highly purified proteins of plant origin) in order to correct pathological processes in the kidneys due to its ability to bring about harmony among processes (sympaticus – catabolism – acidity) or (parasympaticus – anabolism – alkalinity) in sublimate nephropathy (during the stage of anuria – 24 hours, polyuria – 72 hours), during the period of the development of tubulo-interstitial syndrome – 30 days and in chronic Mazugi nephritis (45 days).
The object of the research is to ascertain the potentialities of the protective effect of the NEPHRINE medication on the course of sublimate nephropathy, chronic Mazugi nephritis in rats with the use of the potentialities of the vegetative resonance test “Imedis Test +” and correlation-optical diagnostics under conditions of water diuresis.
By joint efforts we have broadened the functional potentialities of the vegetative resonance test “Imedis Test +” and elaborated a mode of life-time diagnostics of the biological parameters of the tissues of the organs of experimental animals. The advantage of the method in question compared with well-known methods of evaluating biological parameters in the homogenates of the organs of experimental animals lies in the fact that this method does not infringe the issues of bioethics and enables to determine biological parameters in these or other organs and tissues of experimental animals in their lifetime without euthanasia.
Fig.45. A mode of diagnosing the biological parameters in the organ tissues of experimental animals which is distinguished by the fact that the biological parameters are determined by means of the vegetative resonance test “Imedis Test +” via a reproducible biologically active point of a volunteer by means of filtration of a specific frequency spectrum of the organospecimen under study according to the bioindex scale (1 – 21 conventional units) under conditions of an immediate contact of a volunteer and inductor with a fixed experimental animal .
In addition a new mode of diagnostics of the concentration of substances in biological fluids employing the vegetative resonance test “Imedis Test +” has been elaborated. The formula of invention is presented in Fig. 45.
Fig. 45. A mode of diagnosing the concentration of substances in biological fluids which is distinct by the fact that they are determined by means of the vegetative resonance test “Imedis Test +” via a reproducible biologically active point of a volunteer with a direct contact of the latter with the device electrode by placing a specimen with a biological fluid into a test tube made of organic glass in the container of the “Imedis BRT PK” apparatus by using of programs according to the bioindex scale (1 – 21 conventional units).
The application of the method in question enabled to obtain reliable direct correlations between the concentrations of sodium and potassium ions and urinary creatinine when these are evaluated by means of well-known objective methods and the vegetative resonance test technique “Imedis Test +” (Fig. 45).
Fig.45.
Regression analysis among the concentrations of sodium and potassium, ions urinary creatinine that were evaluated by means of well-known methods of investigation sodium ions (mmol/l), potassium (mmol/l) – using the method of flame photometry on FPL-1, creatinine (mmol/l) using the photometric technique with picric acid in the alkaline medium and the method of the vegetative resonance test “Imedis Test +” (conventional units) in case of water induced diuresis and 3% sodium chloride solution load, r – the correlation coefficient, n – the number of observations, p – correlation significance
The NEPHRINE medication caused a tendency towards an elevation of diuresis during the oliguric stage , the urinary concentration of sodium ions, lithium, angiotensin 2, protein, Tx A2, the concentration of urinary mercury increased and the NEPHRINE medication was tested (Fig. 46)
The influence of theNEPHRINE on the course of sublimate nephropathy in rats during the oliguric stage of the development of the pathologic process in 24 hours upon injecting mercury bichloride when studying rats by means of the vegetative resonance test “Imedis Test +”
1 - sublimate nephropathy;
2 - sublimate nephropathy + NEPHRINE
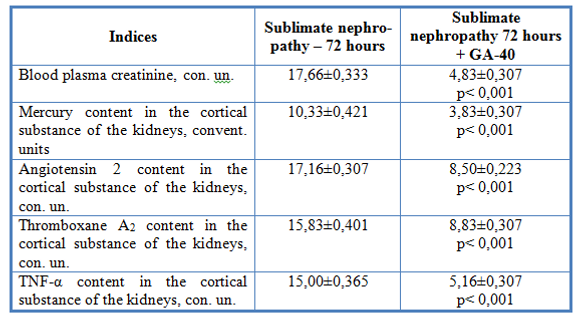
Reliability of differences compared with sublimate nephropathy has been marked ∗∗∗ - p < 0,001. The NEPHRINE diminished the level of retention azotemia during the polyuric stage of sublimate nephropathy, as can be judged by a decrease of the blood plasma creatinine and it decreased the content of mercury, angiotensin 2, thromboxane A2, tumor necrosis factor-α Table 94. The Influence of the NEPHRINE medication on the degree of retention azotemia, the content, of mercury, angiotensin 2, thromboxane A2, TNF-α in the cortical substance of the kidneys at the polyuric stage of sublimate nephropathy while investigating rats with the use of the vegetative resonance test “Imedis Test +” (x ± Sx).
Table 94.
On the 30th day of sublimate nephropathy the formation of tubulo-interstitial syndrome was noted in the cortical, medullary substance and the papilla of the kidneys which was evidenced by an increase of the crystalline substance (as a marker of collagen) and a decrease of the amorphous one (as a reflection of atrophy of the nephron segments). The NEPHRINE preparation exerted an antinephrosclerotic effect under these conditions at the level of all the renal layers the latter being accompanied by a normalization of the level of the amorphous, crystalline substance and their relationship.
Fig. 49. The antinephrosclerotic effect of the GA-40 medical preparation on the development of tubulo-interstitial syndrome (TIS).
On the 45th day of chronic Masugi nephritis an increase of the collagen marker – oxyproline and proapoptic protein p53 was diagnosed in the renal substance (Fig.49). The GA-40 preparation exerted an antinephrosclerotic prophylactic effect under these conditions.
Fig.50.
The protective effect of the GA-40 medical preparation on the development of tubulo-interstitial syndrome on the 45th day of chronic Masugi nephritis according to the findings of testing by means of the vegetative resonance test “Imedis Test +”.
1 – control (intact animals), 2 - tubulo-interstitial syndrome, 3 - tubulo-interstitial syndrome against a background of using the GA-40 medication. The significance of distinctions is marked: ∗∗∗ - p < 0,001 compared with the control; ∗∗∗ - p < 0,001 compared with tubulo-interstitial syndrome on the 45th day of chronic Masugi nephritis.
Discussion:
The protective effect of the GA-40 is due to its ability to bring about harmony among the processes (sympaticus – catabolism – acidity) or (parasympaticus – anabolism – alkalinity), resulting in diminished damage by bichloride of mercury of the proximal portion of the nephron, as evidenced by a urinary mercury increase, a diminished protein concentration, a decrease of urinary sodium and lithium ions (lithium ions are reabsorbed exceptionally in the proximal portion of the nephron). A decrease of the damaging effect of corrosive sublimate on the proximal portion of the nephron is accompanied by a decrease of the delivery of sodium ions to the macula densa of the distal portion of the nephron with diminished reactivity of the tubulo-glomerular feedback and ischemic activation of lipid peroxidation in the renal cortical substance, as indicated by a urinary decrease of angiotensin 2, thromboxane A2. A revealed decrease of the content of mercury and tumor necrosis factor-α in the renal cortical substance during the polyuric stage of sublimate nephropathy are indicative of the protective effect of the GA-40 preparation on the proximal portion of the nephron. This is accompanied by a decrease of the reactivity of the tubulo-interstitial feedback with a decrease of the level of vasoconstrictors of angiotensin 2 and thromboxane A2 in the renal cortical substance with a decrease of the level of retention azotemia on the basis of creatinine in the blood plasma. A decrease of the vasoconstrictive collagen-stimulating potential of angiotensin 2 and thromboxane A2 under the influence of the GA-40 remedy causes its antinephrosclerotic effect during the chronic period of Masugi nephritis, sublimate nephropathy and prevents atrophy of the tubules and glomeruli of the nephron at the expense of apoptotic processes.
Conclusions
-
The GA-40 preparation exerts a protective effect on the course of sublimate nephropathy during both the oliguric and polyuric stages of a pathological process, being accompanied by an accelerated urinary excretion of mercury from the organism, a decrease of its content in the renal cortical substance, a reduction of the degree of retention azotemia at the expense of a normalization of vasoconstrictive collagen-stimulating potential of angiotensin 2 and thromboxane A2, the method of the vegetative resonance test “Imedis Test +” enables to detect the GA-40 preparation in the urine of rats that have been preliminarily injected with it.
-
A decrease of the vasoconstrictive collagen-stimulating potential of angiotensin 2 and thromboxane A2 under the influence of the GA-40 preparation causes its antinephrosclerotic effect during the chronic period of Masugi nephritis, sublimate nephropathy and prevents atrophy of the tubules and glomeruli of the nephron owing to an activation of apoptotic processes.
-
A prospect of research trials envisages further application of the vegetative resonance test “Imedis Test +” for an intravital evaluation of the protective effect of the GA-40 preparation in experimental animals with renal diseases.
7. Pahophysiological Analysis of the Diagnosis of GA-40 Medication Protective Activity During Sublimate Nephropathy in Rats with Vegetative-Resonance Test “Imedis Test+”
Prof. Rohovyy Yurii Evgenyi, Arkhipova Ludmila Georgii, Muraviova Irina Lev, Bocharoff A. V.
Bukovina State Medical University (Tschernovsky), Ukraine, 58001,
E-mail: yuriy_rohovyy@rambler.ru
Center for Intellectual Medical Systems “IMEDIS” (Moscow) of Russian Federation
Purpose of the research: investigation of the diagnostic opportunities of protective abilities of GA-40 preparation during sublimate nephropathy in rats with vegetative-resonance test “Imedis Test+” at water diuresis.
In the experiments with 24 white mail mature rats with sublimate nephropathy (administration of 0.1% sublimate solution at 5 mg/kg dosage), protective effects of GA-40 preparation have been investigated (daily administration at 2 mkg/kg dosage) at oliguric (24 hours) and polyuric (72 hours) stages of acute renal failure.
At oliguric stage of sublimate nephropathy in rats with low sodium group GA-40 preparation caused tendency to increased diuresis with additional decreased content of Creatinin, Sodium ions, Potassium, Lithium, Urea, Thromboxan A2, Aldosterone, protein, PgE2, Angiotensine 2, TNF-α, L-Arginine, vasointestinal peptide in urea. Concentration of sublimate was increased and GA-40 medication tested.
At polyuric stage of sublimate nephropathy GA-40 medication promoted decrease of renal azotermia lowering creatinin concentration in blood plasma, sublimate, Angiotensine 2, Thromboxan A2, TNF-α, L-Arginine, PgE2, VIP in cortex renalis. Correlation analysis revealed primary interconnection between blood creatinin – sublimate of renal cortex and PgE2, sublimate of renal cortex -- TNF-α of kidney cortex.
Protective effect of GA-40 preparation is determined by its ability of harmonized relations among processes (sympathetic – catabolism – acidity) or (parasympathetic – anabolism – alkalinity). As the result, damage of proximal section of the nephrone with sublimate (mercury dichloride) diminishes, which is verified by the increase of sublimate in the urine, decrease of protein content, sodium and lithium ions (lithium ions are re-absorbed exclusively in proximal section of the nephrone). Decrease of the damaging action of sublimate on proximal section of the nephrone is accompanied by the decrease in sodium ions delivery to macula densa distal section of the nephrone with the diminished reactivity of tubulomerular reverse connection (feedback) and ischemic activation of lipid peroxidation in kidney cortex that was indicated decrease of Angiotensine 2 and Thromboxan A2 in urine. Decrease of PgE2, VIP and L-Arginine indicates lowering of vasodilator tone in response to weakened tone of vasoconstrictors Angiotensine 2 and Thromboxan A2. Decrease of creatinin concentration and urea in the urine points to diminished intensity of renal azotermia because of protective influence of GA-40 medication.
Revealed decrease of sublimate content and TNF-α within renal cortex at polyuric stage of sublimate nephropathy points to protective effect of GA-40 medication at proximal section of the nephrone. This is accompanied by lowered reactivity of tubular-glomerular reverse conjunction with the decreased content of vasoconstrictors Angiotensine 2 and Thromboxan A2 in renal cortex with weakened renal azotermia to creatinin content in blood plasma. Lowered content of vasodilators PgE2, VIP and L-Arginine in cortex of the kidneys points not only to the absence of re-perfusional injury of kidneys towards the influence upon GA-40 medication, but, most probably, to polyuric stage itself because of elimination of preliminary complex injury of kidneys against treatment background of the given preparation.
Positive correlative connection between sublimate content and blood creatinin is determined by the development of retentive azotermia because of the damage of proximal nephrone and activation of tubulo-glomelural biofeedback. Primary correlative dependence between PgE2 and TNF-α at polyuric stage of sublimate nephropathy is determined by reperfusional damage of proximal tubule.
Conclusion
1. GA-40 medication has protective influence during sublimate nephropathy both at oliguric and polyuric stages of pathology, accompanied by accelerated sublimate excretion with urine from the organism, decrease of its content in kidney cortex, lower rate of retentive azotermia due to the normalization of the balance of hormonal-messenger systems of sodium-ion homeostasis.
2. Method of vegetative-resonance test “Imedis Test” gives us the possibility to reveal presence of preliminarily administered GA-40 medication in rats’ urine.
8.Analysis of the protective effects of GA-40 medication during sublimate nephropathy with a vegetative resonance test “Imedis Test +”
V.P.Pishak, Yu.E.Rogovy, I.I.Sidorchuk, L.G.Arkhipova, I.L.Muraviyova, A.V.Bocharov, M.V.Khalaturnik.
Bukovina State Medical University (Tschernovsky), Ukraine, 58001,
E-mail: yuriy_rohovyy@rambler.ru
Abstract: Analysis of the protective effects of GA-40 medication on rats during sublimate nephropathy.
Materials and Methods. Protective effect of GA-40 has been investigated in the experiments on 24 mature white mail rats during oliguric and polyuric stages of acute renal failure. Following parameters were determined at bio-index scale in urine assessment with the vegetative resonance test ‘Imedis Test+”: creatinin, ions of Sodium, potassium, lithium, urea, thromboxan A2, aldosterone, protein PgE2, angiotensine 2, TNF-a, L-arginine, vasointestinal peptide, GA-40. Lifetime testing of creatinin in blood and sublimate in cortical substance of the rat kidneys, as well as PgE, angiotensine 2., TNF-a, L-arginine, vasointestinal peptide was performed through the reproductive biologically active point of healthy volunteer.
Results: It has been shown that GA-40 preparation has a protective effect during sublimate nephropathy both at oliguric and polyuric stages of pathology that is entailed by accelerated excretion of sublimate with urine, decrease of it’s abundance within cortical substance of the kidneys, lower rate of retentive azotermia due to normalization of the balance of hormonal-messenger system of sodium-ion homeostasis. The method of the vegetative resonance test “Imedis Test+” makes possible to determine the presence of pre-administered GA-40 preparation in rat’s urine.
Conclusion:
the perspective of scientific investigations lies in permanent use of the vegetative-resonance test “Imedis Test+” for the life-time assessment of biological parameters of experimental animals with kidney diseases.